CUT RESISTANCE STANDARDS
Posted by IRONCLAD PERFORMANCE WEAR on Feb 3rd 2022
ANSI/ISEA 105 CUT RATING
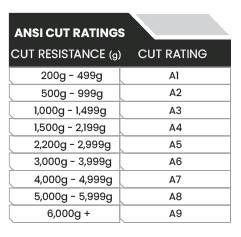
Companies in North America follow guidelines set by the American National Standards Institute, or ANSI, and approved by the International Safety Equipment Association, or ISEA.Ratings are specified in the document titled ANSI/ISEA 105.When testing for glove cut resistance, the following test method is used: ASTM F2992-15.This test is sometimes referred to as the TDM test, after the TDM-100 testing machine used in the test.
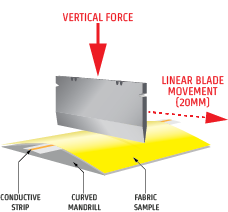
As shown below, the test is performed by placing a fabric sample, taken from the palm of the glove, onto a curved mandrill.A specified vertical force is applied to a razor blade bringing it into contact with the fabric. The blade is then moved across the fabric until cut through is achieved, and the distance traveled is recorded. This process is repeated five times at three different vertical forces, each with a fresh razor blade.The results are charted and a ‘trend line’ is formed.This trend line is used to calculate the amount of force, in grams, required to cause a cut through at 20mm of blade travel.This result, in grams of force, is used to determine the ANSI/ISEA 105 cut rating for the glove, as shown below.
EN 388 CUT RATING
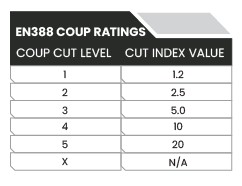
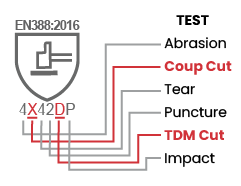
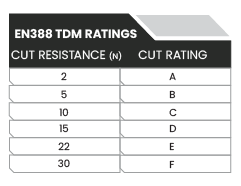
The European Union and many countries outside North America utilize the EN 388:2016 testing standard for evaluating cut resistant gloves.Prior to 2016, this standard utilized a cut testing method known as the Coup Test.With the advent of hardened fibers such as stainless steel, the coup test proved to have a major flaw: hardened fibers will dull the blade and cause the calculations to become dramatically skewed to the point of being useless.Thus, in 2016, the EN 388 standard was updated to include the same TDM test method found in the ANSI/ISEA 105 test method, with forces measured in Newtons instead of grams.This test is performed according to EN ISO 13997; see the table below for the specified cut levels and diagram below for the layout of the EN388:2016 cut rating symbol for mechanical hazards.
COMPARING CUT RATINGS
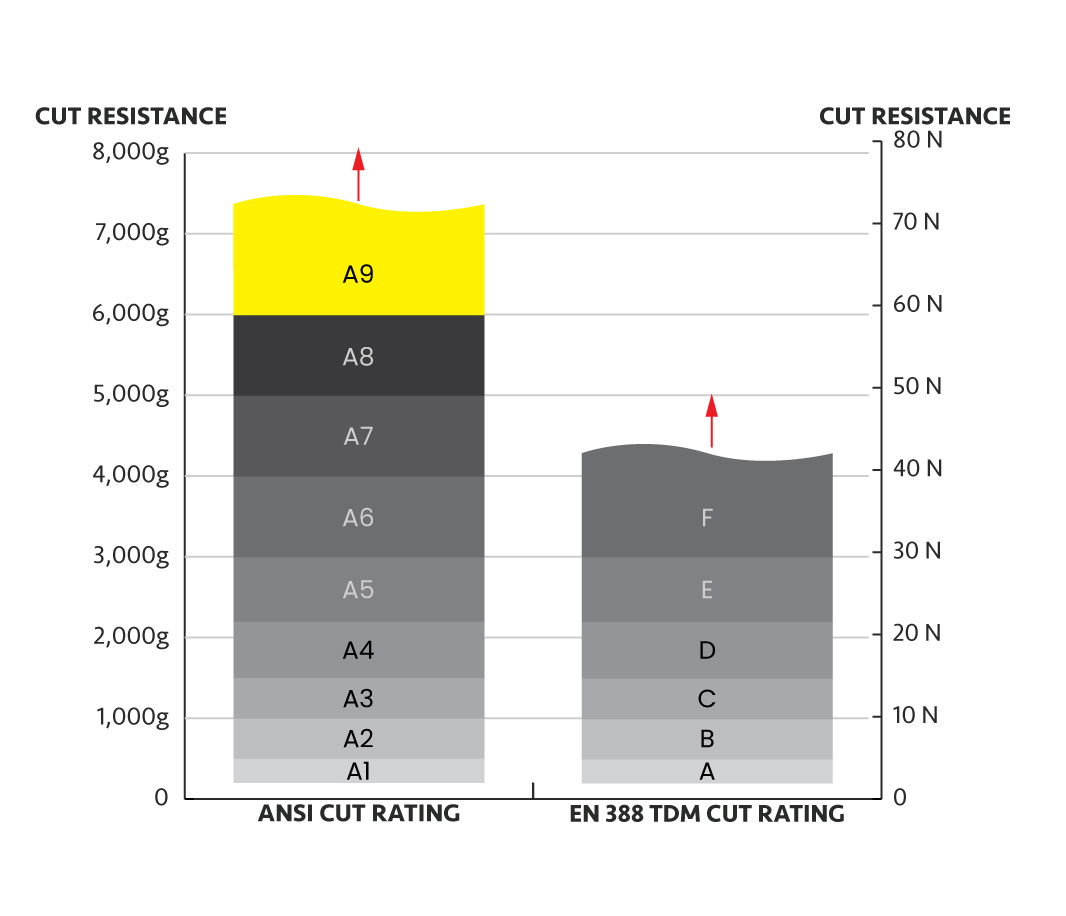
Since both the ANSI/ISEA 105 and EN 388:2016 cut standards utilize the same test method, you can easily compare cut ratings between the two standards, as illustrated below.
COUP TESTING
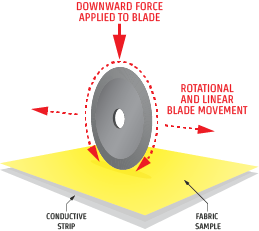
While the coup test has its limitations for testing hardened fibers, it is still required in the EN 388:2016 testing standard. Illustrated below, the coup test is performed by placing a swatch of palm fabric onto a conductive surface and using a circular, counter-rotating blade under a standard 5 Newton load to perform the test. The blade moves back and forth over the material until either cut through is achieved or 60 cycles is reached, and the number of cycles is recorded. This is repeated 5 times, and the average number of rotations is used to determine the coup cut rating – see below.
Note that if the blade becomes dulled during the coup test, then a value of ‘X’ is recorded, and the TDM test must be used to evaluate the cut rating.Some glove manufacturers will perform both tests and provide both test ratings, whether or not the coup test results in a level ‘X’.